-
Quick start
-
API
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Dense
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MutiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- Embedding
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles ( 12 ) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- Embedding
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles ( 12 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Dense
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- SimpleRNN
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- Embedding
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Show All Articles ( 12 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles ( 15 ) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles ( 15 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles ( 15 ) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles ( 15 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
- Add
- AdditiveAttention
- AlphaDropout
- Attention
- Average
- AvgPool1D
- AvgPool2D
- AvgPool3D
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Concatenate
- Conv1D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2D
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3D
- Conv3DTranspose
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Cropping1D
- Cropping2D
- Cropping3D
- Dense
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Dropout
- Embedding
- Flatten
- GaussianDropout
- GaussianNoise
- GlobalAvgPool1D
- GlobalAvgPool2D
- GlobalAvgPool3D
- GlobalMaxPool1D
- GlobalMaxPool2D
- GlobalMaxPool3D
- GRU
- Input
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MaxPool1D
- MaxPool2D
- MaxPool3D
- MultiHeadAttention
- Multiply
- Permute3D
- Reshape
- RNN
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- SimpleRNN
- SpatialDropout
- Substract
- TimeDistributed
- UpSampling1D
- UpSampling2D
- UpSampling3D
- ZeroPadding1D
- ZeroPadding2D
- ZeroPadding3D
- Show All Articles ( 45 ) Collapse Articles
-
- AlphaDropout
- AvgPool1D
- AvgPool2D
- AvgPool3D
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Conv1D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2D
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3D
- Conv3DTranspose
- Cropping1D
- Cropping2D
- Cropping3D
- Dense
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Dropout
- Embedding
- Flatten
- GaussianDropout
- GaussianNoise
- GlobalAvgPool1D
- GlobalAvgPool2D
- GlobalAvgPool3D
- GlobalMaxPool1D
- GlobalMaxPool2D
- GlobalMaxPool3D
- GRU
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MaxPool1D
- MaxPool2D
- MaxPool3D
- Permute3D
- Reshape
- RNN
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- SimpleRNN
- SpatialDropout
- UpSampling1D
- UpSampling2D
- UpSampling3D
- ZeroPadding1D
- ZeroPadding2D
- ZeroPadding3D
- Show All Articles ( 32 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
- Resume
- Accuracy
- BinaryAccuracy
- BinaryCrossentropy
- BinaryIoU
- CategoricalAccuracy
- CategoricalCrossentropy
- CategoricalHinge
- CosineSimilarity
- FalseNegatives
- FalsePositives
- Hinge
- Huber
- IoU
- KLDivergence
- LogCoshError
- Mean
- MeanAbsoluteError
- MeanAbsolutePercentageError
- MeanIoU
- MeanRelativeError
- MeanSquaredError
- MeanSquaredLogarithmicError
- MeanTensor
- OneHotIoU
- OneHotMeanIoU
- Poisson
- Precision
- PrecisionAtRecall
- Recall
- RecallAtPrecision
- RootMeanSquaredError
- SensitivityAtSpecificity
- SparseCategoricalAccuracy
- SparseCategoricalCrossentropy
- SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy
- Specificity
- SpecificityAtSensitivity
- SquaredHinge
- Sum
- TopKCategoricalAccuracy
- TrueNegatives
- TruePositives
- Show All Articles ( 28 ) Collapse Articles
-
- Resume
- Constant
- GlorotNormal
- GlorotUniform
- HeNormal
- HeUniform
- Identity
- LecunNormal
- LecunUniform
- Ones
- Orthogonal
- RandomNormal
- RandomUnifom
- TruncatedNormal
- VarianceScaling
- Zeros
- Show All Articles ( 1 ) Collapse Articles
-
GRU
Description
Define the gru layer according to its parameters. To be used for the TimeDistributed layer. Type : polymorphic.
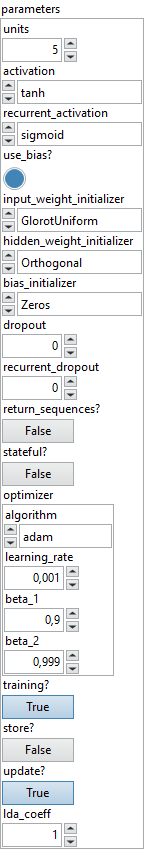
Input parameters
![]() parameters : layer parameters.
parameters : layer parameters.
![]() units : integer, dimensionality of the output space.
units : integer, dimensionality of the output space.![]() activation : enum, activation function to use.
activation : enum, activation function to use.
Default value “tanh”.![]() recurrent_activation : enum, activation function to use for the recurrent step.
recurrent_activation : enum, activation function to use for the recurrent step.
Default value “sigmoid”.![]() use_bias? : boolean, whether the layer uses a bias vector.
use_bias? : boolean, whether the layer uses a bias vector.
Default value “True”.![]() input_weight_initializer : enum, initializer for the kernelweights matrix, used for the linear transformation of the inputs.
input_weight_initializer : enum, initializer for the kernelweights matrix, used for the linear transformation of the inputs.
Default value “glorot_uniform”.![]() hidden_weight_initializer : enum, initializer for the recurrent_kernelweights matrix, used for the linear transformation of the recurrent state.
hidden_weight_initializer : enum, initializer for the recurrent_kernelweights matrix, used for the linear transformation of the recurrent state.
Default value “orthogonal”.![]() bias_initializer : enum, initializer for the bias vector.
bias_initializer : enum, initializer for the bias vector.
Default value “zeros”.![]() dropout : float, fraction of the units to drop for the linear transformation of the inputs.
dropout : float, fraction of the units to drop for the linear transformation of the inputs.
Default value “0.0”.![]() recurrent_dropout : float, fraction of the units to drop for the linear transformation of the recurrent state.
recurrent_dropout : float, fraction of the units to drop for the linear transformation of the recurrent state.
Default value “0.0”.![]() return_sequences? : boolean, whether to return the last output in the output sequence, or the full sequence.
return_sequences? : boolean, whether to return the last output in the output sequence, or the full sequence.
Default value “False”.![]() stateful? : boolean, if True, the last state for each sample at index i in a batch will be used as initial state for the sample of index i in the following batch.
stateful? : boolean, if True, the last state for each sample at index i in a batch will be used as initial state for the sample of index i in the following batch.
Default value “False”.![]() optimizer :
optimizer :
![]() algorithm : enum, (name of optimizer) for optimizer instance.
algorithm : enum, (name of optimizer) for optimizer instance.
Default value “adam”.![]() learning_rate : float, define the learning rate to use.
learning_rate : float, define the learning rate to use.
Default value “0.001”.![]() beta_1 : float, define the exponential decay rate for the 1st moment estimates.
beta_1 : float, define the exponential decay rate for the 1st moment estimates.
Default value “0.9”.![]() beta_2 : float, define the exponential decay rate for the 2nd moment estimates.
beta_2 : float, define the exponential decay rate for the 2nd moment estimates.
Default value “0.999”.
![]() training? : boolean, whether the layer is in training mode (can store data for backward).
training? : boolean, whether the layer is in training mode (can store data for backward).
Default value “True”.![]() store? : boolean, whether the layer stores the last iteration gradient (accessible via the “get_gradients” function).
store? : boolean, whether the layer stores the last iteration gradient (accessible via the “get_gradients” function).
Default value “False”.![]() update? : boolean, whether the layer’s variables should be updated during backward. Equivalent to freeze the layer.
update? : boolean, whether the layer’s variables should be updated during backward. Equivalent to freeze the layer.
Default value “True”.![]() lda_coeff : float, defines the coefficient by which the loss derivative will be multiplied before being sent to the previous layer (since during the backward run we go backwards).
lda_coeff : float, defines the coefficient by which the loss derivative will be multiplied before being sent to the previous layer (since during the backward run we go backwards).
Default value “1”.
Output parameters
![]() GRU out : layer gru architecture.
GRU out : layer gru architecture.
Example
All these exemples are snippets PNG, you can drop these Snippet onto the block diagram and get the depicted code added to your VI (Do not forget to install HAIBAL library to run it).
GRU layer inside TimeDistributed layer
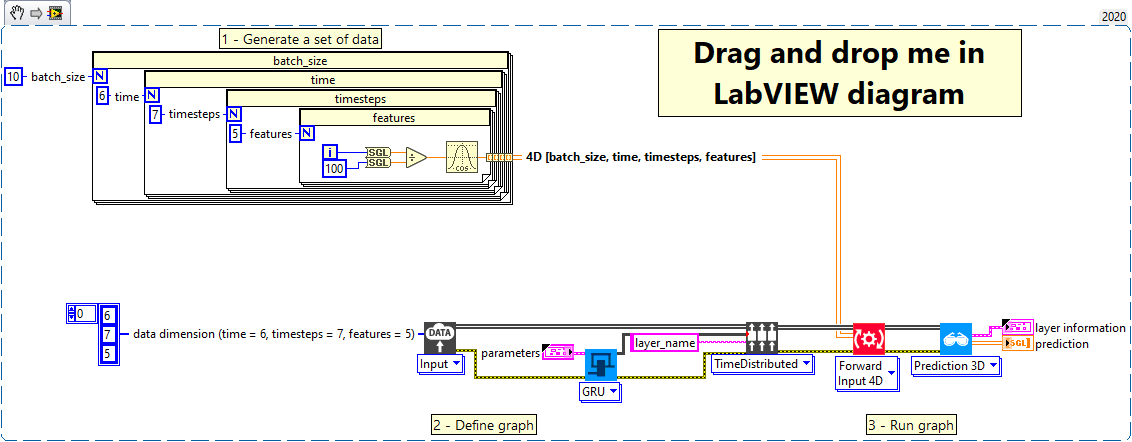
1 – Generate a set of data
We generate an array of data of type single and shape [batch_size = 10, time = 6, timesteps = 7, features = 5].
2 – Define graph
First, we define the first layer of the graph which is an Input layer (explicit input layer method). This layer is setup as an input array shaped [time = 6, timesteps = 7, features = 5].
Then, we add to the graph the TimeDistributed layer which we setup with a GRU layer using the define method.
3 – Run graph
We call the forward method and retrieve the result with the “Prediction 3D” method.
This method returns two variables, the first one is the layer information (cluster composed of the layer name, the graph index and the shape of the output layer) and the second one is the prediction with a shape of [batch_size, time, units].
The output dimension depends on the parameters “return-sequences”, refer to the chapter “Dimension” of “add to graph” documentation.