-
Quick start
-
API
-
-
- Resume
- Add
- AdditiveAttention
- AlphaDropout
- Attention
- Average
- AvgPool1D
- AvgPool2D
- AvgPool3D
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Concatenate
- Conv1D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2D
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3D
- Conv3DTranspose
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Cropping1D
- Cropping2D
- Cropping3D
- Dense
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Dropout
- Embedding
- Flatten
- GaussianDropout
- GaussianNoise
- GlobalAvgPool1D
- GlobalAvgPool2D
- GlobalAvgPool3D
- GlobalMaxPool1D
- GlobalMaxPool2D
- GlobalMaxPool3D
- GRU
- Input
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MaxPool1D
- MaxPool2D
- MaxPool3D
- MultiHeadAttention
- Multiply
- Output Predict
- Output Train
- Permute3D
- Reshape
- RNN
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- SimpleRNN
- SpatialDropout
- Split
- Substract
- UpSampling1D
- UpSampling2D
- UpSampling3D
- ZeroPadding1D
- ZeroPadding2D
- ZeroPadding3D
- Show All Articles ( 48 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
-
- Resume
- Constant
- GlorotNormal
- GlorotUniform
- HeNormal
- HeUniform
- Identity
- LecunNormal
- LecunUniform
- Ones
- Orthogonal
- RandomNormal
- RandomUnifom
- TruncatedNormal
- VarianceScaling
- Zeros
- Show All Articles ( 1 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Dense
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MutiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- Embedding
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles ( 12 ) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- Embedding
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles ( 12 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Dense
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- SimpleRNN
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- Embedding
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Show All Articles ( 12 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles ( 15 ) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles ( 15 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles ( 15 ) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles ( 15 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
- Resume
- Accuracy
- BinaryAccuracy
- BinaryCrossentropy
- BinaryIoU
- CategoricalAccuracy
- CategoricalCrossentropy
- CategoricalHinge
- CosineSimilarity
- FalseNegatives
- FalsePositives
- Hinge
- Huber
- IoU
- KLDivergence
- LogCoshError
- Mean
- MeanAbsoluteError
- MeanAbsolutePercentageError
- MeanIoU
- MeanRelativeError
- MeanSquaredError
- MeanSquaredLogarithmicError
- MeanTensor
- OneHotIoU
- OneHotMeanIoU
- Poisson
- Precision
- PrecisionAtRecall
- Recall
- RecallAtPrecision
- RootMeanSquaredError
- SensitivityAtSpecificity
- SparseCategoricalAccuracy
- SparseCategoricalCrossentropy
- SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy
- Specificity
- SpecificityAtSensitivity
- SquaredHinge
- Sum
- TopKCategoricalAccuracy
- TrueNegatives
- TruePositives
- Show All Articles ( 28 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
Convolution 1D
Description
Setup and add the convolution 1D layer into the model during the definition graph step. Type : polymorphic.
Input parameters
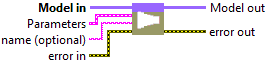
![]() Model in : model architecture
Model in : model architecture
![]() Parameters : layer parameters.
Parameters : layer parameters.
![]() filters : integer, the dimensionality of the output space.
filters : integer, the dimensionality of the output space.
Default value “3”.![]() size : integer, specify the length of the 1D convolution window.
size : integer, specify the length of the 1D convolution window.
Default value “3”.![]() stride : integer, specify the stride length of the convolution.
stride : integer, specify the stride length of the convolution.
Default value “1”.![]() dilation rate : integer, specifying the dilation rate to use for dilated convolution.
dilation rate : integer, specifying the dilation rate to use for dilated convolution.
Default value “1”.![]() explicit padding : array, specifies the number of pixels to pad at the beginning and end of each spatial axis. Batch and channel axes are not padded. Only used when padding = EXPLICIT.
explicit padding : array, specifies the number of pixels to pad at the beginning and end of each spatial axis. Batch and channel axes are not padded. Only used when padding = EXPLICIT.
Default value “empty”.![]() Activation : cluster, activation function to use.
Activation : cluster, activation function to use.![]() use bias? : boolean, whether the layer uses a bias vector.
use bias? : boolean, whether the layer uses a bias vector.
Default value “True”.![]() padding : enum, type of padding to apply.
padding : enum, type of padding to apply.
Default value “VALID”.![]() data format : enum, one of channels_last or channels_first (default) . The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs. channel_last corresponds to inputs with shape (batch, steps, features) while channels_first corresponds to inputs with shape (batch, features, steps).
data format : enum, one of channels_last or channels_first (default) . The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs. channel_last corresponds to inputs with shape (batch, steps, features) while channels_first corresponds to inputs with shape (batch, features, steps).
Default value “channels_first”.![]() Filter Initializer : cluster, initializer for the convolution kernel.
Filter Initializer : cluster, initializer for the convolution kernel.![]() Bias Initializer : cluster, initializer for the bias vector.
Bias Initializer : cluster, initializer for the bias vector.![]() Filter Regularizer : cluster, optional regularizer for the convolution kernel.
Filter Regularizer : cluster, optional regularizer for the convolution kernel.![]() Bias Regularizer : cluster, optional regularizer for the bias vector.
Bias Regularizer : cluster, optional regularizer for the bias vector.![]() training? : boolean, whether the layer is in training mode (can store data for backward).
training? : boolean, whether the layer is in training mode (can store data for backward).
Default value “True”.![]() store? : boolean, whether the layer stores the last iteration gradient (accessible via the “get_gradients” function).
store? : boolean, whether the layer stores the last iteration gradient (accessible via the “get_gradients” function).
Default value “False”.![]() update? : boolean, whether the layer’s variables should be updated during backward. Equivalent to freeze the layer.
update? : boolean, whether the layer’s variables should be updated during backward. Equivalent to freeze the layer.
Default value “True”.![]() lda coeff : float, defines the coefficient by which the loss derivative will be multiplied before being sent to the previous layer (since during the backward run we go backwards).
lda coeff : float, defines the coefficient by which the loss derivative will be multiplied before being sent to the previous layer (since during the backward run we go backwards).
Default value “1”.
![]() name (optional) : string, name of the layer.
name (optional) : string, name of the layer.
Output parameters
![]() Model out : model architecture.
Model out : model architecture.
Dimension
Input shape
3-Dimension tensor with shape : [batch_size, channel, width] (default “channel_first” parameters).
In case of “channel_last” setup, forward function will input shape [batch_size, width, channel].
Output shape
Same shape as input 3-Dimension tensor with shape : [batch_size, channel, width] (default “channel_first” parameters).
In case of “channel_last” setup, forward function will input shape [batch_size, width, channel].
Example
All these exemples are snippets PNG, you can drop these Snippet onto the block diagram and get the depicted code added to your VI (Do not forget to install Deep Learning library to run it).
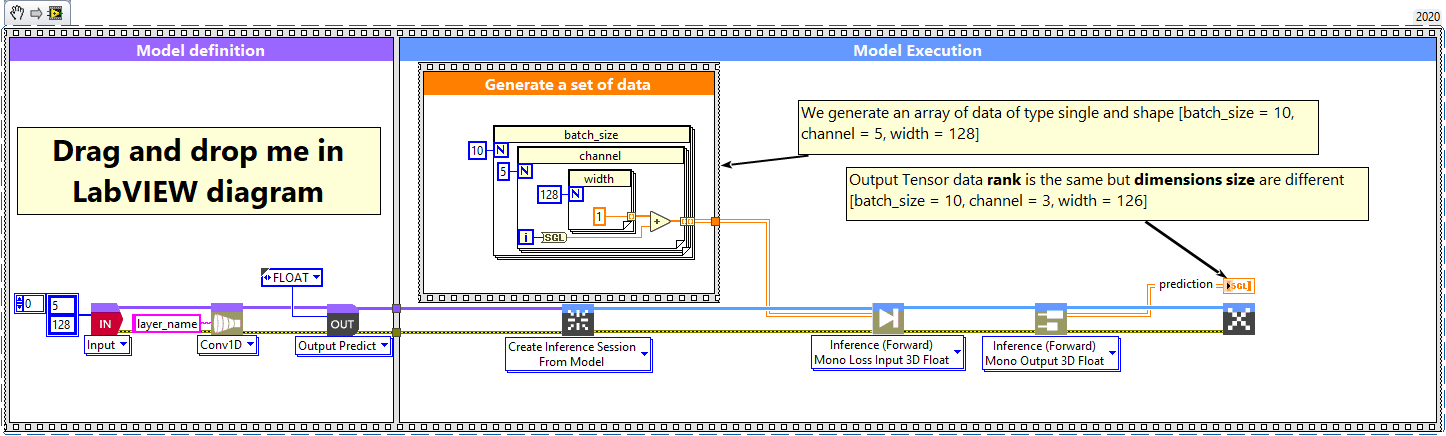
Convolution 1D layer
1 – Generate a set of data
We generate an array of data of type single and shape [batch_size, channel, width] (channel first default layer configuration).
In case of channel last layer configuration, shape is [batch_size, width, channel].
2 – Define graph
First, we define the first layer of the graph which is an Input layer (explicit input layer method). This layer is setup as an input array shaped [channel = 5, width = 128].
Then we add to the graph the Conv1D layer.
3 – Run graph
We call the forward method and retrieve the result with the “Prediction 3D” method.
This method returns two variables, the first one is the layer information (cluster composed of the layer name, the graph index and the shape of the output layer) and the second one is the prediction with a shape of [batch_size, filter, new_width].
Convolution 1D layer, batch and dimension
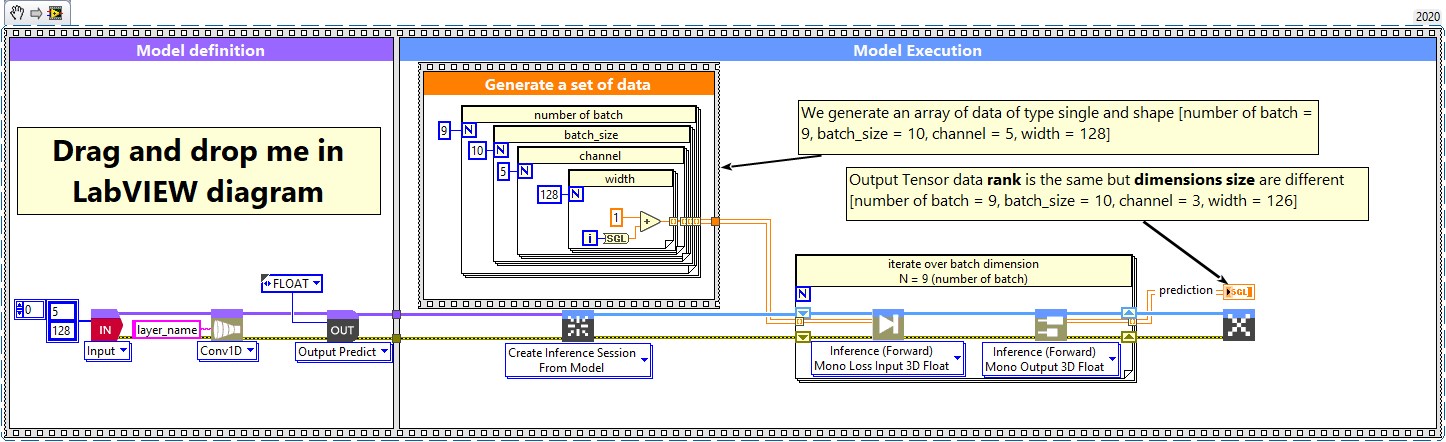
1 – Generate a set of data
We generate an array of data of type single and shape [number of batch = 9, batch_size = 10, channel = 5, width = 128] (channel first default layer configuration).
In case of channel last layer configuration, shape is [batch_size, width, channel].
2 – Define graph
First, we define the first layer of the graph which is an Input layer (explicit input layer method). This layer is setup as an input array shaped [channel = 5, width = 128].
Then we add to the graph the Conv1D layer.
3 – Run graph
We call the forward method and retrieve the result with the “Prediction 3D” method.
This method returns two variables, the first one is the layer information (cluster composed of the layer name, the graph index and the shape of the output layer) and the second one is the prediction with a shape of [batch_size, filter, new_width].