-
Quick start
-
API
-
-
- Resume
- Add
- AdditiveAttention
- AlphaDropout
- Attention
- Average
- AvgPool1D
- AvgPool2D
- AvgPool3D
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Concatenate
- Conv1D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2D
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3D
- Conv3DTranspose
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Cropping1D
- Cropping2D
- Cropping3D
- Dense
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Dropout
- ELU
- Embedding
- Exponential
- Flatten
- GaussianDropout
- GaussianNoise
- GELU
- GlobalAvgPool1D
- GlobalAvgPool2D
- GlobalAvgPool3D
- GlobalMaxPool1D
- GlobalMaxPool2D
- GlobalMaxPool3D
- GRU
- HardSigmoid
- Input
- LayerNormalization
- LeakyReLU
- Linear
- LSTM
- MaxPool1D
- MaxPool2D
- MaxPool3D
- MultiHeadAttention
- Multiply
- Output Predict
- Output Train
- Permute3D
- PReLU
- ReLU
- Reshape
- RNN
- SELU
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- Sigmoid
- SimpleRNN
- SoftMax
- SoftPlus
- SoftSign
- SpatialDropout
- Split
- Substract
- Swish
- TanH
- ThresholdedReLU
- UpSampling1D
- UpSampling2D
- UpSampling3D
- ZeroPadding1D
- ZeroPadding2D
- ZeroPadding3D
- Show All Articles (64) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
- Abs
- Acos
- Acosh
- ArgMax
- ArgMin
- Asin
- Asinh
- Atan
- Atanh
- AveragePool
- Bernouilli
- BitwiseNot
- BlackmanWindow
- Cast
- Ceil
- Celu
- ConcatFromSequence
- Cos
- Cosh
- DepthToSpace
- Det
- DynamicTimeWarping
- Erf
- Exp
- EyeLike
- Flatten
- Floor
- GlobalAveragePool
- GlobalLpPool
- GlobalMaxPool
- HammingWindow
- HannWindow
- HardSwish
- HardMax
- Identity
- ImageDecoder
- Inverse
- lrfft
- lslnf
- lsNaN
- Log
- LogSoftmax
- LpNormalization
- LpPool
- LRN
- MeanVarianceNormalization
- MicrosoftGelu
- Mish
- Multinomial
- MurmurHash3
- Neg
- NhwcMaxPool
- NonZero
- Not
- OptionalGetElement
- OptionalHasElement
- QuickGelu
- RandomNormalLike
- RandomUniformLike
- RawConstantOfShape
- Reciprocal
- ReduceSumInteger
- RegexFullMatch
- Rfft
- Round
- SampleOp
- SequenceLength
- Shape
- Shrink
- Sign
- Sin
- Sinh
- Size
- SpaceToDepth
- Sqrt
- StringNormalizer
- Tan
- TfldfVectorizer
- Tokenizer
- Transpose
- UnfoldTensor
- Show All Articles (66) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
- Add
- AffineGrid
- And
- BiasAdd
- BiasGelu
- BiasSoftmax
- BiasSplitGelu
- BitShift
- BitwiseAnd
- BitwiseOr
- BitwiseXor
- CastLike
- CDist
- CenterCropPad
- Clip
- Col2lm
- ComplexMul
- ComplexMulConj
- Compress
- Conv
- ConvInteger
- ConvTranspose
- ConvTransposeWithDynamicPads
- CropAndResize
- CumSum
- DeformConv
- DequantizeBFP
- DequantizeLinear
- DequantizeWithOrder
- DFT
- Div
- DynamicQuantizeMatMul
- Equal
- Expand
- ExpandDims
- FastGelu
- FusedConv
- FusedGemm
- FusedMatMul
- FusedMatMulActivation
- GatedRelativePositionBias
- Gather
- GatherElements
- GatherND
- Gemm
- GemmFastGelu
- GemmFloat8
- Greater
- GreaterOrEqual
- GreedySearch
- GridSample
- GroupNorm
- InstanceNormalization
- Less
- LessOrEqual
- LongformerAttention
- MatMul
- MatMulBnb4
- MatMulFpQ4
- MatMulInteger
- MatMulInteger16
- MatMulIntergerToFloat
- MatMulNBits
- MaxPoolWithMask
- MaxRoiPool
- MaxUnPool
- MelWeightMatrix
- MicrosoftDequantizeLinear
- MicrosoftGatherND
- MicrosoftGridSample
- MicrosoftPad
- MicrosoftQLinearConv
- MicrosoftQuantizeLinear
- MicrosoftRange
- MicrosoftTrilu
- Mod
- MoE
- Mul
- MulInteger
- NegativeLogLikelihoodLoss
- NGramRepeatBlock
- NhwcConv
- NhwcFusedConv
- NonMaxSuppression
- OneHot
- Or
- PackedAttention
- PackedMultiHeadAttention
- Pad
- Pow
- QGemm
- QLinearAdd
- QLinearAveragePool
- QLinearConcat
- QLinearConv
- QLinearGlobalAveragePool
- QLinearLeakyRelu
- QLinearMatMul
- QLinearMul
- QLinearReduceMean
- QLinearSigmoid
- QLinearSoftmax
- QLinearWhere
- QMoE
- QOrderedAttention
- QOrderedGelu
- QOrderedLayerNormalization
- QOrderedLongformerAttention
- QOrderedMatMul
- QuantizeLinear
- QuantizeWithOrder
- Range
- ReduceL1
- ReduceL2
- ReduceLogSum
- ReduceLogSumExp
- ReduceMax
- ReduceMean
- ReduceMin
- ReduceProd
- ReduceSum
- ReduceSumSquare
- RelativePositionBias
- Reshape
- Resize
- RestorePadding
- ReverseSequence
- RoiAlign
- RotaryEmbedding
- ScatterElements
- ScatterND
- SequenceAt
- SequenceErase
- SequenceInsert
- Slice
- SparseToDenseMatMul
- SplitToSequence
- Squeeze
- STFT
- StringConcat
- Sub
- Tile
- TorchEmbedding
- TransposeMatMul
- Trilu
- Unsqueeze
- Where
- WordConvEmbedding
- Xor
- Show All Articles (134) Collapse Articles
-
- Attention
- AttnLSTM
- BatchNormalization
- BiasDropout
- BifurcationDetector
- BitmaskBiasDropout
- BitmaskDropout
- DecoderAttention
- DecoderMaskedMultiHeadAttention
- DecoderMaskedSelfAttention
- Dropout
- DynamicQuantizeLSTM
- EmbedLayerNormalization
- GemmaRotaryEmbedding
- GroupQueryAttention
- GRU
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MicrosoftMultiHeadAttention
- QAttention
- RemovePadding
- RNN
- Sampling
- SkipGroupNorm
- SkipLayerNormalization
- SkipSimplifiedLayerNormalization
- SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss
- SparseAttention
- TopK
- WhisperBeamSearch
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Resume
- Constant
- GlorotNormal
- GlorotUniform
- HeNormal
- HeUniform
- Identity
- LecunNormal
- LecunUniform
- Ones
- Orthogonal
- RandomNormal
- RandomUnifom
- TruncatedNormal
- VarianceScaling
- Zeros
- Show All Articles (1) Collapse Articles
-
- Resume
- BinaryCrossentropy
- CategoricalCrossentropy
- CategoricalHinge
- CosineSimilarity
- Hinge
- Huber
- KLDivergence
- LogCosh
- MeanAbsoluteError
- MeanAbsolutePercentageError
- MeanSquaredError
- MeanSquaredLogarithmicError
- Poisson
- SquaredHinge
- Custom
- Show All Articles (1) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
-
- Dense
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MutiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- Embedding
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (12) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- Embedding
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (12) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Resume
- Dense
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- SimpleRNN
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- Embedding
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Show All Articles (13) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Resume
- Accuracy
- BinaryAccuracy
- BinaryCrossentropy
- BinaryIoU
- CategoricalAccuracy
- CategoricalCrossentropy
- CategoricalHinge
- CosineSimilarity
- FalseNegatives
- FalsePositives
- Hinge
- Huber
- IoU
- KLDivergence
- LogCoshError
- Mean
- MeanAbsoluteError
- MeanAbsolutePercentageError
- MeanIoU
- MeanRelativeError
- MeanSquaredError
- MeanSquaredLogarithmicError
- MeanTensor
- OneHotIoU
- OneHotMeanIoU
- Poisson
- Precision
- PrecisionAtRecall
- Recall
- RecallAtPrecision
- RootMeanSquaredError
- SensitivityAtSpecificity
- SparseCategoricalAccuracy
- SparseCategoricalCrossentropy
- SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy
- Specificity
- SpecificityAtSensitivity
- SquaredHinge
- Sum
- TopKCategoricalAccuracy
- TrueNegatives
- TruePositives
- Show All Articles (28) Collapse Articles
-
-
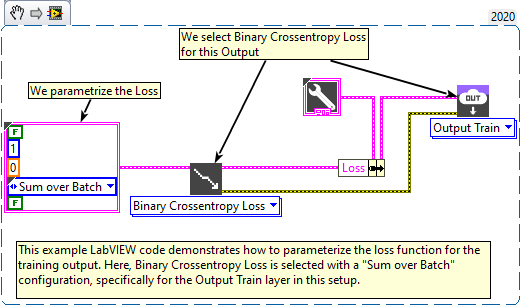
Huber
Description
Computes the Huber loss between y_true and y_pred. Type : polymorphic.
![]()
Input parameters
![]() Parameters : cluster,
Parameters : cluster,
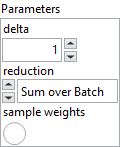
![]() delta : float, the point where the Huber loss function changes from a quadratic to linear.
delta : float, the point where the Huber loss function changes from a quadratic to linear.![]() reduction : enum, type of reduction to apply to the loss. In almost all cases this should be “Sum over Batch“.
reduction : enum, type of reduction to apply to the loss. In almost all cases this should be “Sum over Batch“.![]() sample weights : boolean, if enabled, adds an input for weighting each sample individually.
sample weights : boolean, if enabled, adds an input for weighting each sample individually.
Output parameters
![]() Loss : cluster, this cluster defines the loss function used for model training.
Loss : cluster, this cluster defines the loss function used for model training.
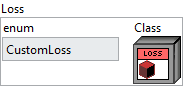
![]() enum : enum, an enumeration indicating the loss type (e.g., MSE, CrossEntropy, etc.). If
enum : enum, an enumeration indicating the loss type (e.g., MSE, CrossEntropy, etc.). If enum is set to CustomLoss, the custom class on the right will be used as the loss function. Otherwise, the selected loss will be applied with its default configuration.![]() Class : object, a custom loss class instance.
Class : object, a custom loss class instance.
Required data
![]() y_pred : array, predicted values.
y_pred : array, predicted values.![]() y_true : array, true values.
y_true : array, true values.
Use cases
Huber loss is a loss function commonly used in regression. It combines the advantages of mean squared error (MSE) and mean absolute error (MAE) to create a loss function that is less sensitive to outliers. For small errors, it acts like an MSE, favoring accuracy, and for large errors, it becomes similar to an MAE, reducing sensitivity to extreme values. This characteristic makes it particularly useful in cases where the data contains outliers or significant errors.
Example
All these exemples are snippets PNG, you can drop these Snippet onto the block diagram and get the depicted code added to your VI (Do not forget to install Deep Learning library to run it).