-
Quick start
-
API
-
-
- Resume
- Add
- AdditiveAttention
- AlphaDropout
- Attention
- Average
- AvgPool1D
- AvgPool2D
- AvgPool3D
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Concatenate
- Conv1D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2D
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3D
- Conv3DTranspose
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Cropping1D
- Cropping2D
- Cropping3D
- Dense
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Dropout
- ELU
- Embedding
- Exponential
- Flatten
- GaussianDropout
- GaussianNoise
- GELU
- GlobalAvgPool1D
- GlobalAvgPool2D
- GlobalAvgPool3D
- GlobalMaxPool1D
- GlobalMaxPool2D
- GlobalMaxPool3D
- GRU
- HardSigmoid
- Input
- LayerNormalization
- LeakyReLU
- Linear
- LSTM
- MaxPool1D
- MaxPool2D
- MaxPool3D
- MultiHeadAttention
- Multiply
- Output Predict
- Output Train
- Permute3D
- PReLU
- ReLU
- Reshape
- RNN
- SELU
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- Sigmoid
- SimpleRNN
- SoftMax
- SoftPlus
- SoftSign
- SpatialDropout
- Split
- Substract
- Swish
- TanH
- ThresholdedReLU
- UpSampling1D
- UpSampling2D
- UpSampling3D
- ZeroPadding1D
- ZeroPadding2D
- ZeroPadding3D
- Show All Articles (64) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
- Abs
- Acos
- Acosh
- ArgMax
- ArgMin
- Asin
- Asinh
- Atan
- Atanh
- AveragePool
- Bernouilli
- BitwiseNot
- BlackmanWindow
- Cast
- Ceil
- Celu
- ConcatFromSequence
- Cos
- Cosh
- DepthToSpace
- Det
- DynamicTimeWarping
- Erf
- Exp
- EyeLike
- Flatten
- Floor
- GlobalAveragePool
- GlobalLpPool
- GlobalMaxPool
- HammingWindow
- HannWindow
- HardSwish
- HardMax
- Identity
- ImageDecoder
- Inverse
- lrfft
- lslnf
- lsNaN
- Log
- LogSoftmax
- LpNormalization
- LpPool
- LRN
- MeanVarianceNormalization
- MicrosoftGelu
- Mish
- Multinomial
- MurmurHash3
- Neg
- NhwcMaxPool
- NonZero
- Not
- OptionalGetElement
- OptionalHasElement
- QuickGelu
- RandomNormalLike
- RandomUniformLike
- RawConstantOfShape
- Reciprocal
- ReduceSumInteger
- RegexFullMatch
- Rfft
- Round
- SampleOp
- SequenceLength
- Shape
- Shrink
- Sign
- Sin
- Sinh
- Size
- SpaceToDepth
- Sqrt
- StringNormalizer
- Tan
- TfldfVectorizer
- Tokenizer
- Transpose
- UnfoldTensor
- Show All Articles (66) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
- Add
- AffineGrid
- And
- BiasAdd
- BiasGelu
- BiasSoftmax
- BiasSplitGelu
- BitShift
- BitwiseAnd
- BitwiseOr
- BitwiseXor
- CastLike
- CDist
- CenterCropPad
- Clip
- Col2lm
- ComplexMul
- ComplexMulConj
- Compress
- Conv
- ConvInteger
- ConvTranspose
- ConvTransposeWithDynamicPads
- CropAndResize
- CumSum
- DeformConv
- DequantizeBFP
- DequantizeLinear
- DequantizeWithOrder
- DFT
- Div
- DynamicQuantizeMatMul
- Equal
- Expand
- ExpandDims
- FastGelu
- FusedConv
- FusedGemm
- FusedMatMul
- FusedMatMulActivation
- GatedRelativePositionBias
- Gather
- GatherElements
- GatherND
- Gemm
- GemmFastGelu
- GemmFloat8
- Greater
- GreaterOrEqual
- GreedySearch
- GridSample
- GroupNorm
- InstanceNormalization
- Less
- LessOrEqual
- LongformerAttention
- MatMul
- MatMulBnb4
- MatMulFpQ4
- MatMulInteger
- MatMulInteger16
- MatMulIntergerToFloat
- MatMulNBits
- MaxPoolWithMask
- MaxRoiPool
- MaxUnPool
- MelWeightMatrix
- MicrosoftDequantizeLinear
- MicrosoftGatherND
- MicrosoftGridSample
- MicrosoftPad
- MicrosoftQLinearConv
- MicrosoftQuantizeLinear
- MicrosoftRange
- MicrosoftTrilu
- Mod
- MoE
- Mul
- MulInteger
- NegativeLogLikelihoodLoss
- NGramRepeatBlock
- NhwcConv
- NhwcFusedConv
- NonMaxSuppression
- OneHot
- Or
- PackedAttention
- PackedMultiHeadAttention
- Pad
- Pow
- QGemm
- QLinearAdd
- QLinearAveragePool
- QLinearConcat
- QLinearConv
- QLinearGlobalAveragePool
- QLinearLeakyRelu
- QLinearMatMul
- QLinearMul
- QLinearReduceMean
- QLinearSigmoid
- QLinearSoftmax
- QLinearWhere
- QMoE
- QOrderedAttention
- QOrderedGelu
- QOrderedLayerNormalization
- QOrderedLongformerAttention
- QOrderedMatMul
- QuantizeLinear
- QuantizeWithOrder
- Range
- ReduceL1
- ReduceL2
- ReduceLogSum
- ReduceLogSumExp
- ReduceMax
- ReduceMean
- ReduceMin
- ReduceProd
- ReduceSum
- ReduceSumSquare
- RelativePositionBias
- Reshape
- Resize
- RestorePadding
- ReverseSequence
- RoiAlign
- RotaryEmbedding
- ScatterElements
- ScatterND
- SequenceAt
- SequenceErase
- SequenceInsert
- Slice
- SparseToDenseMatMul
- SplitToSequence
- Squeeze
- STFT
- StringConcat
- Sub
- Tile
- TorchEmbedding
- TransposeMatMul
- Trilu
- Unsqueeze
- Where
- WordConvEmbedding
- Xor
- Show All Articles (134) Collapse Articles
-
- Attention
- AttnLSTM
- BatchNormalization
- BiasDropout
- BifurcationDetector
- BitmaskBiasDropout
- BitmaskDropout
- DecoderAttention
- DecoderMaskedMultiHeadAttention
- DecoderMaskedSelfAttention
- Dropout
- DynamicQuantizeLSTM
- EmbedLayerNormalization
- GemmaRotaryEmbedding
- GroupQueryAttention
- GRU
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MicrosoftMultiHeadAttention
- QAttention
- RemovePadding
- RNN
- Sampling
- SkipGroupNorm
- SkipLayerNormalization
- SkipSimplifiedLayerNormalization
- SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss
- SparseAttention
- TopK
- WhisperBeamSearch
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Resume
- Constant
- GlorotNormal
- GlorotUniform
- HeNormal
- HeUniform
- Identity
- LecunNormal
- LecunUniform
- Ones
- Orthogonal
- RandomNormal
- RandomUnifom
- TruncatedNormal
- VarianceScaling
- Zeros
- Show All Articles (1) Collapse Articles
-
- Resume
- BinaryCrossentropy
- CategoricalCrossentropy
- CategoricalHinge
- CosineSimilarity
- Hinge
- Huber
- KLDivergence
- LogCosh
- MeanAbsoluteError
- MeanAbsolutePercentageError
- MeanSquaredError
- MeanSquaredLogarithmicError
- Poisson
- SquaredHinge
- Custom
- Show All Articles (1) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
-
- Dense
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MutiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- Embedding
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (12) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- Embedding
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (12) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Resume
- Dense
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- SimpleRNN
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- Embedding
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Show All Articles (13) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Resume
- Accuracy
- BinaryAccuracy
- BinaryCrossentropy
- BinaryIoU
- CategoricalAccuracy
- CategoricalCrossentropy
- CategoricalHinge
- CosineSimilarity
- FalseNegatives
- FalsePositives
- Hinge
- Huber
- IoU
- KLDivergence
- LogCoshError
- Mean
- MeanAbsoluteError
- MeanAbsolutePercentageError
- MeanIoU
- MeanRelativeError
- MeanSquaredError
- MeanSquaredLogarithmicError
- MeanTensor
- OneHotIoU
- OneHotMeanIoU
- Poisson
- Precision
- PrecisionAtRecall
- Recall
- RecallAtPrecision
- RootMeanSquaredError
- SensitivityAtSpecificity
- SparseCategoricalAccuracy
- SparseCategoricalCrossentropy
- SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy
- Specificity
- SpecificityAtSensitivity
- SquaredHinge
- Sum
- TopKCategoricalAccuracy
- TrueNegatives
- TruePositives
- Show All Articles (28) Collapse Articles
-
-
MicrosoftGridSample
Description
Given an input and a flow-field grid, computes the output using input values and pixel locations from grid. Currently, only spatial (4-D) inputs are supported. For input with shape (N, C, H, W) and grid with shape (N, H_out, W_out, 2), the output will have shape (N, C, H_out, W_out). For each output location output[n, :, h, w], the size-2 vector grid[n, h, w] specifies input pixel locations x and y, which are used to interpolate the output value output[n, :, h, w]. The GridSample operator is often used in doing grid generator and sampler in the Spatial Transformer Networks. See also in torch.nn.functional.grid_sample.
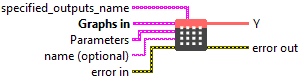
Input parameters
![]() specified_outputs_name : array, this parameter lets you manually assign custom names to the output tensors of a node.
specified_outputs_name : array, this parameter lets you manually assign custom names to the output tensors of a node.
![]() Graphs in : cluster, ONNX model architecture.
Graphs in : cluster, ONNX model architecture.
![]() X (heterogeneous) – T1 : object, 4-D tensor of shape (N, C, H, W), where N is the batch size, C is the numbers of channels, H and W are the height and width of the input data.
X (heterogeneous) – T1 : object, 4-D tensor of shape (N, C, H, W), where N is the batch size, C is the numbers of channels, H and W are the height and width of the input data.![]() grid (heterogeneous) – T1 : object, input offset, 4-D tensor of shape (N, H_out, W_out, 2), where H_out and W_out are the height and width of grid and output, Grid specifies the sampling pixel locations normalized by the input spatial dimensions. Therefore, it should have most values in the range of [-1, 1]. If grid has values outside the range of [-1, 1], the corresponding outputs will be handled as defined by padding_mode.
grid (heterogeneous) – T1 : object, input offset, 4-D tensor of shape (N, H_out, W_out, 2), where H_out and W_out are the height and width of grid and output, Grid specifies the sampling pixel locations normalized by the input spatial dimensions. Therefore, it should have most values in the range of [-1, 1]. If grid has values outside the range of [-1, 1], the corresponding outputs will be handled as defined by padding_mode.

![]() Parameters : cluster,
Parameters : cluster,
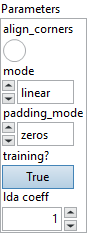
![]() align_corners : boolean, if align_corners=true, the extrema (-1 and 1) are considered as referring to the center points of the input’s corner pixels. If align_corners=false, they are instead considered as referring to the corner points of the input’s corner pixels, making the sampling more resolution agnostic.
align_corners : boolean, if align_corners=true, the extrema (-1 and 1) are considered as referring to the center points of the input’s corner pixels. If align_corners=false, they are instead considered as referring to the corner points of the input’s corner pixels, making the sampling more resolution agnostic.
Default value “False”.![]() mode : enum, three interpolation modes.
mode : enum, three interpolation modes.
Default value “bilinear”.![]() padding_mode : enum, support padding modes for outside grid values. zeros: use 0 for out-of-bound grid locations, border: use border values for out-of-bound grid locations, reflection: use values at locations reflected by the border for out-of-bound grid locations.
padding_mode : enum, support padding modes for outside grid values. zeros: use 0 for out-of-bound grid locations, border: use border values for out-of-bound grid locations, reflection: use values at locations reflected by the border for out-of-bound grid locations.
Default value “zeros”.![]() training? : boolean, whether the layer is in training mode (can store data for backward).
training? : boolean, whether the layer is in training mode (can store data for backward).
Default value “True”.![]() lda coeff : float, defines the coefficient by which the loss derivative will be multiplied before being sent to the previous layer (since during the backward run we go backwards).
lda coeff : float, defines the coefficient by which the loss derivative will be multiplied before being sent to the previous layer (since during the backward run we go backwards).
Default value “1”.
![]() name (optional) : string, name of the node.
name (optional) : string, name of the node.
Output parameters
![]() Y (heterogeneous) – T2 : object, 4-D tensor of shape (N, C, H_out, W_out).
Y (heterogeneous) – T2 : object, 4-D tensor of shape (N, C, H_out, W_out).
Type Constraints
T1 in (tensor(uint8), tensor(uint16), tensor(uint32), tensor(uint64), tensor(int8), tensor(int16), tensor(int32),tensor(int64), tensor(float16), tensor(float), tensor(double), tensor(string), tensor(bool), tensor(complex64), tensor(complex128)) : Constrain input types to all tensor types.
T2 in (tensor(double), tensor(float), tensor(float16)) : Constrain output types to float tensors.

